What Is Software Update Com Sec Android Fotaclient Android
Implement In-app Update In Android
Make sure every user of your app is on the new version.
![]()
In this article, we will learn about the In-app update feature in Android what is all about In-app update, what are the benefits of using the In-app update in your android application. Recently I've been working on a product in which I need to Implement an In-app update Why we need to Implement this?.
As a Developer we always want our users to have the updated version of their application but there are a lot of people who actually turned off their auto update from google play store and he/she doesn't know about any update available or not.
To overcome the problem Google Introduced this feature called In-app update from this feature you can easily prompt the user to update the application and with the user permission you can update the application also while updating the app user can be able to interact with the application. Now the user doesn't need to go to google play store to check there is any update available or not.
What is In-App Update:
An In-app update was Introduced as a part of the Play Core Library, which actually allows you to prompts the user to update the application when there is any update available on the Google Play Store.
There are two modes of an In-app update.
- Flexible Update
- Immediate Update
Flexible Update:
In Flexible update, the dialog will appear and after the update, the user can interact with the application.
This mode is recommended to use when there is no major change In your application like some features that don't affect the core functionality of your application.
The update of the application is downloading in the background in the flexible update and after the completion of the downloading, the user will see the dialog in which the user needs to restart the application. The dialog will not automatically show, we need to check and show to the user and we will learn how later.
Benefits:
The major benefit of the flexible update is the user can interact with the application.
Example Of Flexible Update:
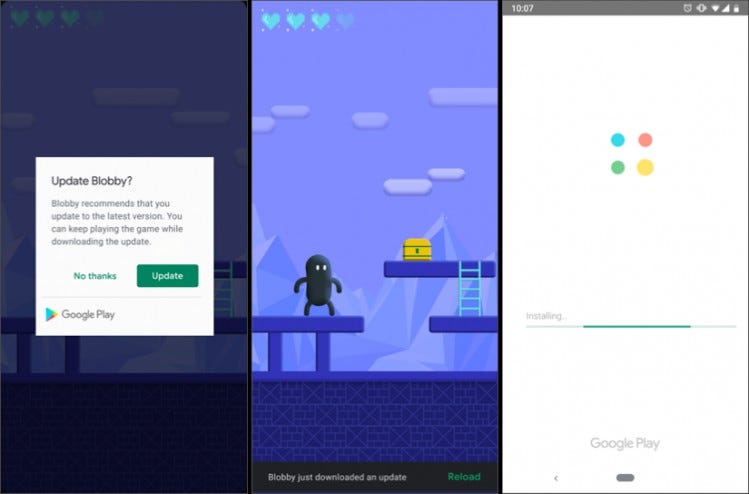
Immediate Update:
In Immediate Update the fullscreen UI come up in our application and the user can't interact with the application and after the update the application restart it-self and updated the application.
This mode is recommended when your app update affects directly the core functionality, Like when you have any critical update, so this mode we need to use.
Example Of Immediate Update:
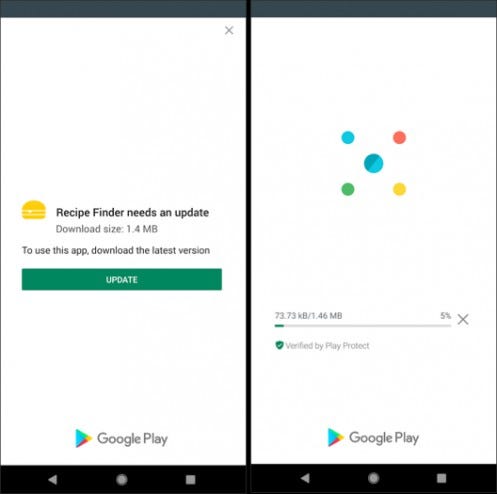
In-app updates works only with devices running Android 5.0 (API level 21) or higher, and requires you to use Play Core library 1.5.0 or higher
Implementation:
Let's start with the In-App update implementation, what we need to do first.
Step 1: Add Dependency
Add the Google Play Core Dependency to your android build.gradle file, like the below code snippet.
implementation 'com.google.android.play:core:1.6.4' Note: At the time of writing, the latest play core version was 1.6.4 but you can use any latest stable release you want from Play Core Library.
Step 2: Create an AppManager Instance
We need to create an instance of the AppManager to get the in-app update info, you can define this in your OnCreate method like below code snippet:
// Creates instance of the manager.
private val appUpdateManager: AppUpdateManager? = AppUpdateManagerFactory.create(activity) Step 3: Check for the Update
Now we need to check the update is available or not, before going to request for the update, Like below code snippet:
In the above code, I created a function with the name checkUpdate() in which I first get the app update information using the appUpdateManager instance which I was created earlier, in step 2, & assigned to another variable called appUpdateInfoTask now everything seems perfectly going good, and now we have the info available we just need to add a listener to check whether the new update is available or not.
In addOnSuccessListener we need to first check If update available or not with the function updateAvailability() this will return the Boolean value, and also set the mode Flexible | Immediate. If both the condition meets then we have the update available and we are good to go for the update request.
Step 4: Request for the Update
In Step 4 we will learn how to request for the update, To update the request we need to use AppUpdateManager.startUpdateFlowForResult() like the below code snippet:
In the above code, with startUpdateFlowForResult function we can request the update, in which we need to pass some params.
- appUpdateInfo -> Pass the intent that is returned by
getAppUpdateInfo()function - AppUpdateType.FLEXIBLE -> This is a mode for an update, you can set IMMEDIATE | FLEXIBLE
- this -> current activity making the update request
- MY_REQUEST_CODE -> This is a request code to monitor the update request, in the
OnActivityResultwill discuss this below.
Step 5: Monitor the Update
Now after following the above steps, you will see the update dialog come up, In which you have two options No Thanks | Update button, like the below screenshot.
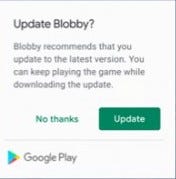
After clicking the update button, the update will start in the background, after the download begins you need to monitor the update when the update can be installed and to display the progress in your app's UI. So for that, we need to register the listener the get the status update. like the below code snippet:
In the above code, the InstallStateUpdateListener will give us the status, when the status is equal to Downloaded, we need to show a notification to the user to restart the application.
Register the Listener
First register the listener before starting the update, like the below code:
// Before starting an update, register a listener for updates.
appUpdateManager.registerListener(listener) UnRegister the Listener
when there is no need longer for the listener then we need to unregister the listener, to avoid the memory leak. like the below code:
// When status updates are no longer needed, unregister the listener.
appUpdateManager.unregisterListener(listener) Note: Monitoring the update state is required for only flexible downloads
Step 6: Complete the Update for Flexible mode
After monitoring the update status and you detect the InstallStatus.DOWNLOADED state. Now you need to restart the app to install the update so for that we need to just call completeUpdate() function like the below code snippet:
appUpdateManager!!.completeUpdate() And after the complete update, the app will restart and now you are in the new version of the application.
Step 7: Monitor the Immediate mode update
Now in the above step, we monitored the update status and handled the cases, for Flexible update mode, now in this step we need to handle the Immediate mode update status.
If the user sets the mode to Immediate then Google play will show the fullscreen UI, and the user can't interact with the application, and after the update begins the update will start in the background and during this period if user's leaves the application and come back again we have to show the updated progress like the below code snippet.
// Checks that the update is not stalled during 'onResume()'.
// However, you should execute this check at all entry points into the app.
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume() appUpdateManager
.appUpdateInfo
.addOnSuccessListener { appUpdateInfo ->
...
if (appUpdateInfo.updateAvailability()
== UpdateAvailability.DEVELOPER_TRIGGERED_UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS
) {
// If an in-app update is already running, resume the update.
appUpdateManager.startUpdateFlowForResult(
appUpdateInfo,
IMMEDIATE,
this,
MY_REQUEST_CODE
);
}
}
}
In the above code, we need to check this in onResume() method, If mode is Immediate & when your app returns to the foreground, you should confirm that the update is not stalled in the UpdateAvailability.DEVELOPER_TRIGGERED_UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS state. If the update is stalled in this state, resume the update, as shown in the above code.
Step 8: Handle Cancel update.
If users cancel the update during the update or before requesting the download. So don't worry as I mentioned above about the override method, OnActivityResult In the startUpdateFlowForResult method, we pass the REQUEST_CODE param.
So when the user's cancel the update onActivityResult called and In this override method we have these three callbacks:
-
RESULT_OK: The user has accepted the update successfully. -
RESULT_CANCELED: The user has canceled the update. -
ActivityResult.RESULT_IN_APP_UPDATE_FAILED: Some other error occurred or the failure of the In-App update.
fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) {
// super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data)
if (requestCode == InAppUpdateConstant.REQUEST_CODE) {
when (resultCode) {
Activity.RESULT_OK -> {
Log.d(TAG, "" + "Result Ok")
// handle user's approval }
}
Activity.RESULT_CANCELED -> {
{ //if you want to request the update again just call checkUpdate()
}
Log.d(TAG, "" + "Result Cancelled")
// handle user's rejection }
}
ActivityResult.RESULT_IN_APP_UPDATE_FAILED -> {
//if you want to request the update again just call checkUpdate()
Log.d(TAG, "" + "Update Failure")
// handle update failure
}
}
}
}
How to Test:
Now the last thing is how to test this, this is a tricky part, the following things for testing you need to be followed.
I divided it into two parts.
Part1
- Generate a signed APK for Production.
- Go to App-Internal-Sharing and upload the build over there, and share the link with the tester
- Now install that build with the shareable link.
Part2
- Generate a signed APK for Production with another version code and version name, make sure the version which you upload earlier is lower than this.
- Go to App-Internal-Sharing and upload the build over there, and share the link with the tester.
- Now click to that link and don't click to the Update button.
- Now just open the application which you installed earlier, you will get the update dialog.
Every time you upload the Build make sure you close the Google Play Store App
Conclusion
This article taught you how to Implement an in-App update in your android application with the two different modes, one is Flexible and one is Immediate, how you can request again, how to monitor the status of the update, and how to test with the Internal app-sharing.
I hope this article is helpful. If you think something is missing, have questions, or would like to offer any thoughts or suggestions, go ahead and leave a comment below. I'd appreciate the feedback.
I've written some other Android-related content, and if you liked what you read here, you'll probably also enjoy these:
If you want to read more about, check out the official developer documentation below:
Sharing (knowledge) is caring 😊 Thanks for reading this article. Be sure to clap or recommend this article if you found it helpful. It means a lot to me.
If you need any help then Join me on Twitter, LinkedIn, GitHub , and Subscribe to my Youtube Channel.
What Is Software Update Com Sec Android Fotaclient Android
Source: https://medium.com/android-news/implement-in-app-update-in-android-68892bd11e35
0 Response to "What Is Software Update Com Sec Android Fotaclient Android"
Post a Comment